CONTINUOUS REDUCTION OF POSTOPERATIVE COMPLICATIONS
Contact usTHYROID SURGERY
There have been cases of accidental damage to the parathyroid glands in thyroid surgery. Since these glands secrete parathyroid hormone (PTH) to control the level of calcium in the blood and bones, it is vital that they are preserved. Removal of the parathyroid glands results in lifelong treatment and regular follow-ups. This may have a significant impact on the patient’s quality of life.
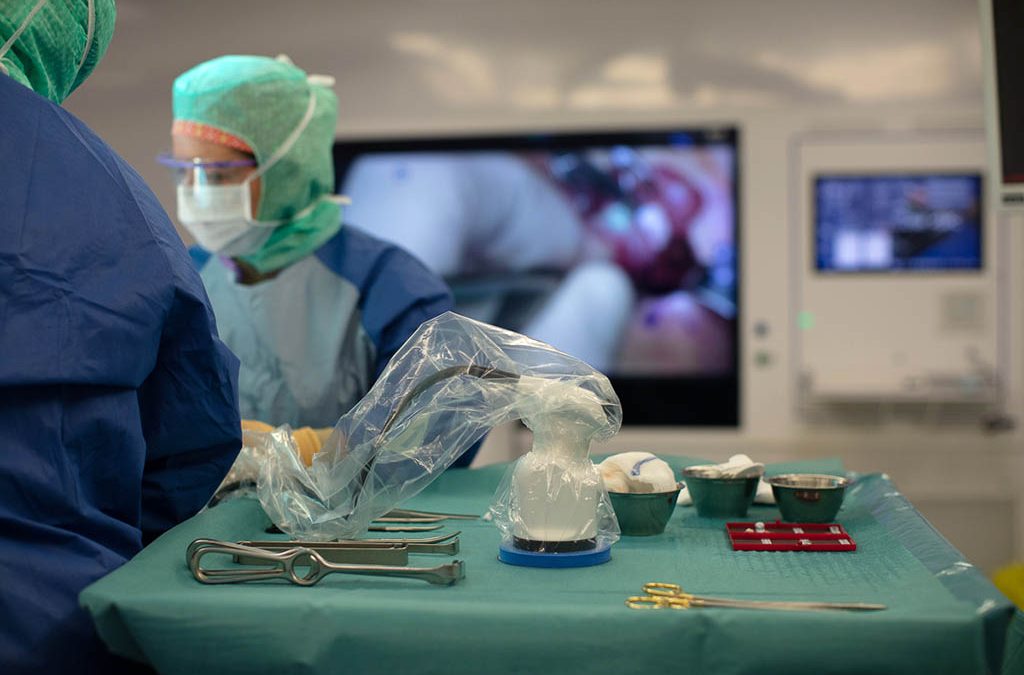
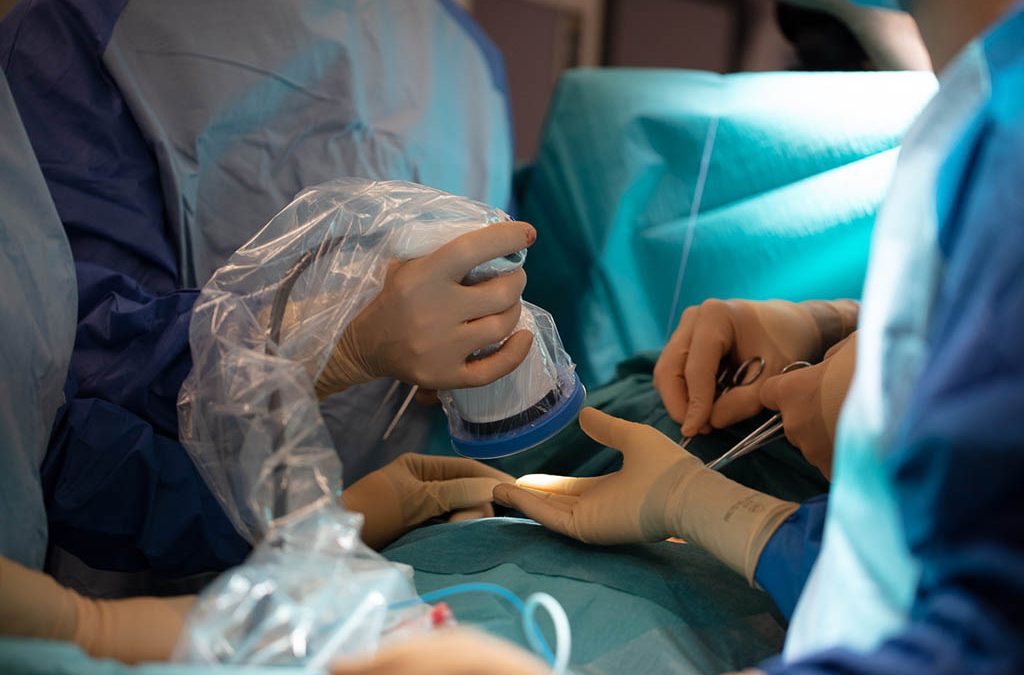
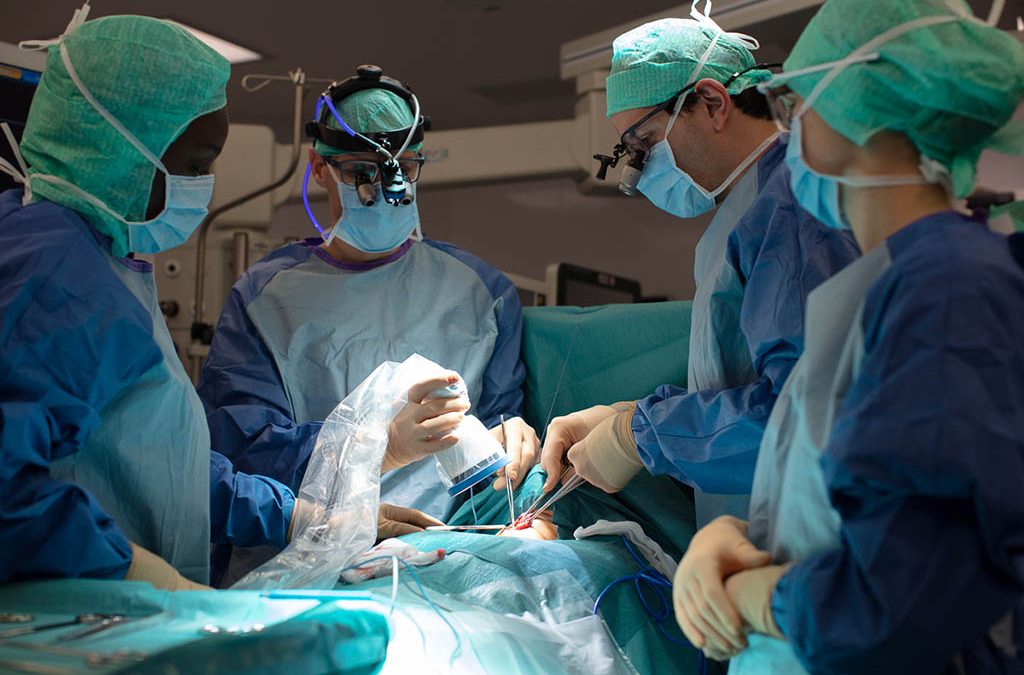
FLUOPTICS® imaging technique helps surgeons to achieve improved visualization of the parathyroid glands. Several independent clinical studies show that complications can be significantly reduced by using our systems.
MOST READ ARTICLES

How is thyroid cancer detected and diagnosed?
Thyroid cancer is increasingly common. Learn about the different types of thyroid cancer, stages of the disease and treatments available.
How does thyroid cancer progress?
Thyroid cancer is increasingly common. Learn about the different types of thyroid cancer, stages of the disease and treatments available.
Thyroid Gland Removal in 6 Questions
Thyroidectomy, or removal of all or part of the thyroid gland, is a frequent but delicate procedure. Learn about the operation and how to prepare for it.
Hyperparathyroidism Treatment: Everything You Need to Know
Do you or someone you know suffer from hyperparathyroidism? Learn about this endocrine disease and existing treatments.
FOCUS ON HEALTH: YOU ARE CONCERNED
Thyroid: what are the risks of surgery
Are you scheduled to undergo thyroid surgery and mulling over the potential complications? Any type of surgery has its risks and is always a cause for concern. In France, each year, 10,000 cases of thyroid cancer are diagnosed and 45,000 people have a thyroidectomy...
Fluorescence benefits for hepatic surgery
HEPATOFLUO: A prospective monocentric study assessing the benefits of indocyanine green (ICG) fluorescence for hepatic surgery. Patrice Peyrat MD1,2; Ellen Blanc PhD3; Stéphanie Guillermet MSc4; Yao Chen MD2; Céline Ferlay MSc3; David Perol MD, PhD3; Valéria...
Use of methylene blue and near-infrared fluorescence
Use of methylene blue and near-infrared fluorescence in thyroid and parathyroid surgery Hillary SL - Langenbecks Arch Surg. 2017 Dec 11. doi: 10.1007/s00423-017-1641-2. Sheffield Teaching Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust, c/o Room F25, Royal Hallamshire Hospital,...
The benefict of near-infrared for lymphatic surgery
Investigating the short-term effects of manual lymphatic drainage and compression garment therapies on lymphatic function using near-infrared imaging Lopera C - Lymphat Res Biol. 2017 Sep;15(3):235-240. doi: 10.1089/lrb.2017.0001. Epub 2017 Jul 27. Clinical Academic...
Vascularized lymph node transfer as a surgical treatment
Intratissue lymphovenous communications in the mechanism of action of vascularized lymph node transfer Miranda Garcés M - J Surg Oncol. 2017 Jan;115(1):27-31. doi: 10.1002/jso.24413. Epub 2016 Nov 25. Department of Plastic Surgery, Hospital de la Santa Creu i Sant...
The use of near-infrared imaging for parathyroid surgery
Intraoperative near-infrared imaging for parathyroid gland identification by autofluorescence: A feasibility study De Leeuw F - World J Surg. 2016 Sep;40(9):2131-8. doi: 10.1007/s00268-016-3571-5. Plateforme d'Imagerie et Cytométrie, UMS AMMICa, Gustave Roussy,...
Identification of autofluorescent parathyroid glands
Cutting edge in thyroid surgery: Autofluorescence of parathyroid glands Falco J - J Am Coll Surg. 2016 Aug;223(2):374-80. doi: 10.1016/j.jamcollsurg.2016.04.049. Epub 2016 May 20. Hospital de Clínicas "José de San Martín", University of Buenos Aires, Buenos Aires,...
Indocyanine green fluorescence and parathyroid autofluorescence
Comparison of indocyanine green fluorescence and parathyroid autofluorescence imaging in the identification of parathyroid glands during thyroidectomy Kahramangil B, Berber E. - Gland Surg. 2017 Dec;6(6):644-648. doi: 10.21037/gs.2017.09.04. Department of Endocrine...
Indocyanine green advantages for the detection of free-flap vascular complications
Indocyanine green fluorescence angiography for free flap monitoring: A pilot study Hitier M. J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 2016 Nov;44(11):1833-1841. doi: 10.1016/j.jcms.2016.09.001. Epub 2016 Sep 10. Plastic and Maxillofacial Surgery Department, Hôpital A Michallon,...
TECHNOLOGY: HOW DOES IT WORK?
Reduction of temporary hypocalcemia
The ability of FLUOBEAM® LX to provide improved protection of the parathyroid glands and their functions has been documented by several clinical teams working with the technology. Findings indicate that early use of autofluorescence in thyroid surgery can result in a significant reduction of transient post-operative hypocalcemia.
Reduction of inadvertent resections
Using autofluorescence facilitates the identification of the parathyroid glands, which in turn makes it possible to preserve them more successfully.
An adapted postoperative management
Fluorescence imaging enables surgeons to analyze the risk of potential hypocalcemia as well as to check and confirm that the parathyroid glands are well perfused at the end of the procedure. This verification is enabled by fluorescence imaging using indocyanine green injection (ICG).
Preserving only one out of four parathyroid glands may be sufficient to regulate blood calcium levels, which in turn may avoid additional postoperative treatment.
YOUR MOST FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS
I am going to have surgery. Which hospitals are equipped with your system?
To access the list of hospitals equipped with our fluorescence imaging solution contact us via this form.
FLUOBEAM® LX is intended to provide real-time near infrared (NIR) fluorescence imaging of tissue during surgical procedures. The FLUOBEAM® LX is intended to assist in the imaging of parathyroid glands and can be used as an adjunctive method to assist in the location of parathyroid glands due to the auto-fluorescence of this tissue. The FLUOBEAM® LX is indicated for use in capturing and viewing fluorescent images for the visual assessment of blood flow in adults as an adjunctive method for the evaluation of tissue perfusion. This is a class II medical device. Product manufactured by FLUOPTICS SAS, France. For proper use, please read carefully all instructions in the specific instructions for use for each product.




